Lab 05 - Implement Intersite Connectivity
Student lab manual
Note: This lab uses Powershell to setup the Virtual Network Gateway and Local Network Gateway. You can also implement a Site-to-Site VPN using the demo provided in the VILT.
Lab scenario
Contoso has its datacenters in Boston, New York, and Seattle offices connected via a mesh wide-area network links, with full connectivity between them. You need to implement a lab environment that will reflect the topology of the Contoso’s on-premises networks and verify its functionality.
Objectives
In this lab, you will:
- Task 1: Provision the lab environment
- Task 2: Configure local and global virtual network peering
- Task 3: Test intersite connectivity
Estimated timing: 30 minutes
Architecture diagram
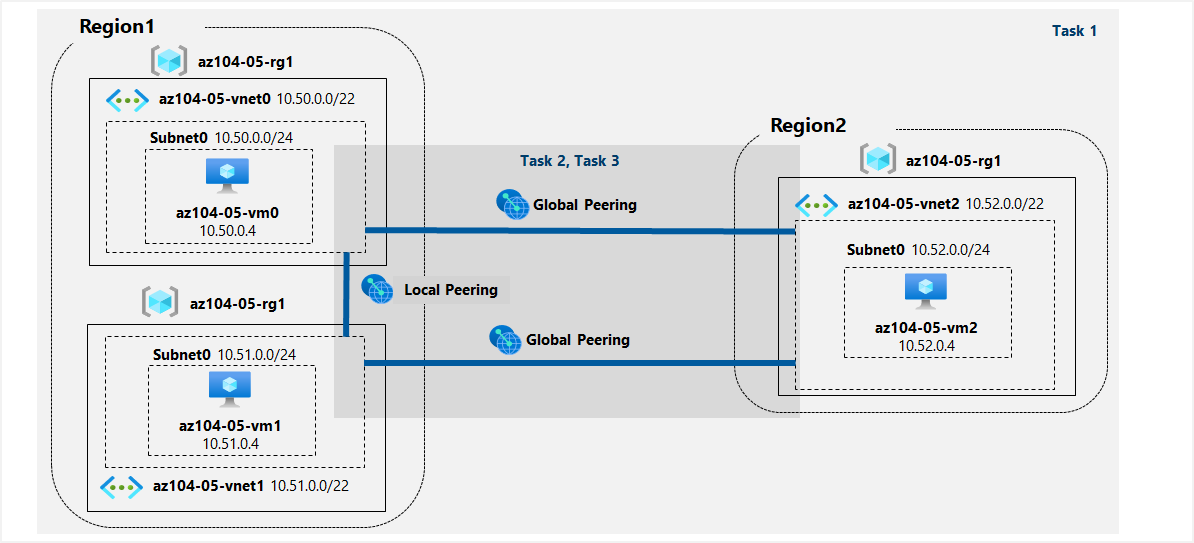
Instructions
Task 1: Provision the lab environment
In this task, you will deploy three virtual machines, each into a separate virtual network, with two of them in the same Azure region and the third one in another Azure region.
-
Sign in to the Azure portal.
-
In the Azure portal, open the Azure Cloud Shell by clicking on the icon in the top right of the Azure Portal.
-
If prompted to select either Bash or PowerShell, select PowerShell.
Note: If this is the first time you are starting Cloud Shell and you are presented with the You have no storage mounted message, select the subscription you are using in this lab, and click Create storage.
-
In the toolbar of the Cloud Shell pane, click the Upload/Download files icon, in the drop-down menu, click Upload and upload the files \Allfiles\Labs\05\az104-05-vnetvm-loop-template.json and \Allfiles\Labs\05\az104-05-vnetvm-loop-parameters.json into the Cloud Shell home directory.
-
Edit the Parameters file you just uploaded and change the password. If you need help editing the file in the Shell please ask your instructor for assistance. As a best practice, secrets, like passwords, should be more securely stored in the Key Vault.
-
From the Cloud Shell pane, run the following to create the resource group that will be hosting the lab environment. The first two virtual networks and a pair of virtual machines will be deployed in
[Azure_region_1]. The third virtual network and the third virtual machine will be deployed in the same resource group but another[Azure_region_2]. (replace the[Azure_region_1]and[Azure_region_2]placeholder with the names of two different Azure regions where you intend to deploy these Azure virtual machines):$location1 = '[Azure_region_1]' $location2 = '[Azure_region_2]' $rgName = 'az104-05-rg1' New-AzResourceGroup -Name $rgName -Location $location1Note: In order to identify Azure regions, from a PowerShell session in Cloud Shell, run (Get-AzLocation).Location
-
From the Cloud Shell pane, run the following to create the three virtual networks and deploy virtual machines into them by using the template and parameter files you uploaded:
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment ` -ResourceGroupName $rgName ` -TemplateFile $HOME/az104-05-vnetvm-loop-template.json ` -TemplateParameterFile $HOME/az104-05-vnetvm-loop-parameters.json ` -location1 $location1 ` -location2 $location2Note: Wait for the deployment to complete before proceeding to the next step. This should take about 2 minutes.
-
Close the Cloud Shell pane.
Task 2: Configure local and global virtual network peering
In this task, you will configure local and global peering between the virtual networks you deployed in the previous tasks.
-
In the Azure portal, search for and select Virtual networks.
-
Review the virtual networks you created in the previous task and verify that the first two are located in the same Azure region and the third one in a different Azure region.
Note: The template you used for deployment of the three virtual networks ensures that the IP address ranges of the three virtual networks do not overlap.
-
In the list of virtual networks, click az104-05-vnet0.
-
On the az104-05-vnet0 virtual network blade, in the Settings section, click Peerings and then click + Add.
-
Add a peering with the following settings (leave others with their default values) and click Add:
Setting Value This virtual network: Peering link name az104-05-vnet0_to_az104-05-vnet1 This virtual network: Traffic to remote virtual network Allow (default) This virtual network: Traffic forwarded from remote virtual network Block traffic that originates from outside this virtual network Virtual network gateway None Remote virtual network: Peering link name az104-05-vnet1_to_az104-05-vnet0 Virtual network deployment model Resource manager I know my resource ID unselected Subscription the name of the Azure subscription you are using in this lab Virtual network az104-05-vnet1 Traffic to remote virtual network Allow (default) Traffic forwarded from remote virtual network Block traffic that originates from outside this virtual network Virtual network gateway None Note: This step establishes two local peerings - one from az104-05-vnet0 to az104-05-vnet1 and the other from az104-05-vnet1 to az104-05-vnet0.
Note: In case you run into an issue with the Azure portal interface not displaying the virtual networks created in the previous task, you can configure peering by running the following PowerShell commands from Cloud Shell:
$rgName = 'az104-05-rg1' $vnet0 = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name 'az104-05-vnet0' -ResourceGroupName $rgname $vnet1 = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name 'az104-05-vnet1' -ResourceGroupName $rgname Add-AzVirtualNetworkPeering -Name 'az104-05-vnet0_to_az104-05-vnet1' -VirtualNetwork $vnet0 -RemoteVirtualNetworkId $vnet1.Id Add-AzVirtualNetworkPeering -Name 'az104-05-vnet1_to_az104-05-vnet0' -VirtualNetwork $vnet1 -RemoteVirtualNetworkId $vnet0.Id -
On the az104-05-vnet0 virtual network blade, in the Settings section, click Peerings and then click + Add.
-
Add a peering with the following settings (leave others with their default values) and click Add:
Setting Value This virtual network: Peering link name az104-05-vnet0_to_az104-05-vnet2 This virtual network: Traffic to remote virtual network Allow (default) This virtual network: Traffic forwarded from remote virtual network Block traffic that originates from outside this virtual network Virtual network gateway None Remote virtual network: Peering link name az104-05-vnet2_to_az104-05-vnet0 Virtual network deployment model Resource manager I know my resource ID unselected Subscription the name of the Azure subscription you are using in this lab Virtual network az104-05-vnet2 Traffic to remote virtual network Allow (default) Traffic forwarded from remote virtual network Block traffic that originates from outside this virtual network Virtual network gateway None Note: This step establishes two global peerings - one from az104-05-vnet0 to az104-05-vnet2 and the other from az104-05-vnet2 to az104-05-vnet0.
Note: In case you run into an issue with the Azure portal interface not displaying the virtual networks created in the previous task, you can configure peering by running the following PowerShell commands from Cloud Shell:
$rgName = 'az104-05-rg1' $vnet0 = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name 'az104-05-vnet0' -ResourceGroupName $rgname $vnet2 = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name 'az104-05-vnet2' -ResourceGroupName $rgname Add-AzVirtualNetworkPeering -Name 'az104-05-vnet0_to_az104-05-vnet2' -VirtualNetwork $vnet0 -RemoteVirtualNetworkId $vnet2.Id Add-AzVirtualNetworkPeering -Name 'az104-05-vnet2_to_az104-05-vnet0' -VirtualNetwork $vnet2 -RemoteVirtualNetworkId $vnet0.Id -
Navigate back to the Virtual networks blade and, in the list of virtual networks, click az104-05-vnet1.
-
On the az104-05-vnet1 virtual network blade, in the Settings section, click Peerings and then click + Add.
-
Add a peering with the following settings (leave others with their default values) and click Add:
Setting Value This virtual network: Peering link name az104-05-vnet1_to_az104-05-vnet2 This virtual network: Traffic to remote virtual network Allow (default) This virtual network: Traffic forwarded from remote virtual network Block traffic that originates from outside this virtual network Virtual network gateway None Remote virtual network: Peering link name az104-05-vnet2_to_az104-05-vnet1 Virtual network deployment model Resource manager I know my resource ID unselected Subscription the name of the Azure subscription you are using in this lab Virtual network az104-05-vnet2 Traffic to remote virtual network Allow (default) Traffic forwarded from remote virtual network Block traffic that originates from outside this virtual network Virtual network gateway None Note: This step establishes two global peerings - one from az104-05-vnet1 to az104-05-vnet2 and the other from az104-05-vnet2 to az104-05-vnet1.
Note: In case you run into an issue with the Azure portal interface not displaying the virtual networks created in the previous task, you can configure peering by running the following PowerShell commands from Cloud Shell:
$rgName = 'az104-05-rg1' $vnet1 = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name 'az104-05-vnet1' -ResourceGroupName $rgname $vnet2 = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name 'az104-05-vnet2' -ResourceGroupName $rgname Add-AzVirtualNetworkPeering -Name 'az104-05-vnet1_to_az104-05-vnet2' -VirtualNetwork $vnet1 -RemoteVirtualNetworkId $vnet2.Id Add-AzVirtualNetworkPeering -Name 'az104-05-vnet2_to_az104-05-vnet1' -VirtualNetwork $vnet2 -RemoteVirtualNetworkId $vnet1.Id
Task 3: Test intersite connectivity
In this task, you will test connectivity between virtual machines on the three virtual networks that you connected via local and global peering in the previous task.
-
In the Azure portal, search for and select Virtual machines.
-
In the list of virtual machines, click az104-05-vm0.
-
On the az104-05-vm0 blade, click Connect, in the drop-down menu, click RDP, on the Connect with RDP blade, click Download RDP File and follow the prompts to start the Remote Desktop session.
Note: This step refers to connecting via Remote Desktop from a Windows computer. On a Mac, you can use Remote Desktop Client from the Mac App Store and on Linux computers you can use an open source RDP client software.
Note: You can ignore any warning prompts when connecting to the target virtual machines.
-
When prompted, sign in by using the Student username and the password from your parameters file.
-
Within the Remote Desktop session to az104-05-vm0, right-click the Start button and, in the right-click menu, click Windows PowerShell (Admin).
-
In the Windows PowerShell console window, run the following to test connectivity to az104-05-vm1 (which has the private IP address of 10.51.0.4) over TCP port 3389:
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName 10.51.0.4 -Port 3389 -InformationLevel 'Detailed'Note: The test uses TCP 3389 since this is this port is allowed by default by operating system firewall.
-
Examine the output of the command and verify that the connection was successful.
-
In the Windows PowerShell console window, run the following to test connectivity to az104-05-vm2 (which has the private IP address of 10.52.0.4):
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName 10.52.0.4 -Port 3389 -InformationLevel 'Detailed' -
Switch back to the Azure portal on your lab computer and navigate back to the Virtual machines blade.
-
In the list of virtual machines, click az104-05-vm1.
-
On the az104-05-vm1 blade, click Connect, in the drop-down menu, click RDP, on the Connect with RDP blade, click Download RDP File and follow the prompts to start the Remote Desktop session.
Note: This step refers to connecting via Remote Desktop from a Windows computer. On a Mac, you can use Remote Desktop Client from the Mac App Store and on Linux computers you can use an open source RDP client software.
Note: You can ignore any warning prompts when connecting to the target virtual machines.
-
When prompted, sign in by using the Student username and the password from your parameters file.
-
Within the Remote Desktop session to az104-05-vm1, right-click the Start button and, in the right-click menu, click Windows PowerShell (Admin).
-
In the Windows PowerShell console window, run the following to test connectivity to az104-05-vm2 (which has the private IP address of 10.52.0.4) over TCP port 3389:
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName 10.52.0.4 -Port 3389 -InformationLevel 'Detailed'Note: The test uses TCP 3389 since this is this port is allowed by default by operating system firewall.
-
Examine the output of the command and verify that the connection was successful.
Clean up resources
Note: Remember to remove any newly created Azure resources that you no longer use. Removing unused resources ensures you will not see unexpected charges.
Note: Don’t worry if the lab resources cannot be immediately removed. Sometimes resources have dependencies and take a longer time to delete. It is a common Administrator task to monitor resource usage, so just periodically review your resources in the Portal to see how the cleanup is going.
-
In the Azure portal, open the PowerShell session within the Cloud Shell pane.
-
List all resource groups created throughout the labs of this module by running the following command:
Get-AzResourceGroup -Name 'az104-05*' -
Delete all resource groups you created throughout the labs of this module by running the following command:
Get-AzResourceGroup -Name 'az104-05*' | Remove-AzResourceGroup -Force -AsJobNote: The command executes asynchronously (as determined by the -AsJob parameter), so while you will be able to run another PowerShell command immediately afterwards within the same PowerShell session, it will take a few minutes before the resource groups are actually removed.
Review Questions
- Can you use a Site-to-Site VPN to connect two Virtual Networks? What is the difference between using a Site-to-Site VPN vs Peering to connect two Virtual Networks in Azure?
- For high availability, what mode of Site-to-Site VPN Gateway should you configure?
Review
In this lab, you have:
- Provisioned the lab environment
- Configured local and global virtual network peering
- Tested intersite connectivity